Dermal Infusion & Structural Remodelling System (SRS Treatment)
One of the most effective ways to deliver active ingredients, antioxidants and medications into the cells and the extracellular matrix is via electrotherapies. For decades, the medical fraternity and the aesthetics industries have used and celebrated the non-invasive effectiveness of applying currents or ultrasound to the skin for maximum absorption of preparations and to regenerate and reanimate biological functions and muscle tone.
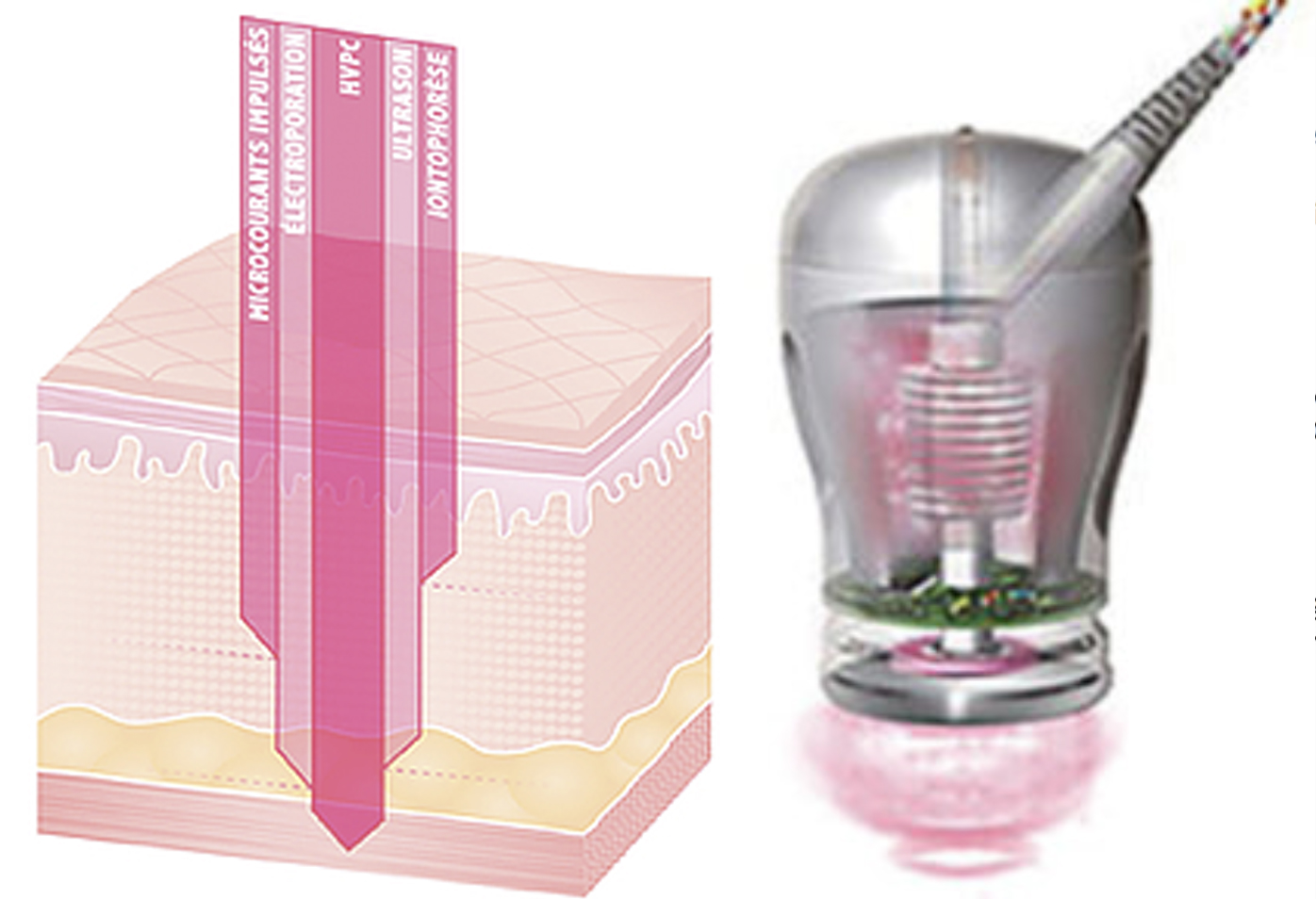
Transdermal delivery of ingredients works in a unique way and is dependant on the type of modality of electrotherapy and the molecular weight of the ingredients. The SRS Skin Remodelling System has unique technology where 5 modes of electrotherapy are combined into one handpiece - maximising the effects by creating a synergy between how the energy is delivered.
The SRS is the first transdermal delivery system to simultaneously combine the compounded effects of HVPC, Impulse micro-currents, ultrasound, electroporation and iontophoresis current.
The technology in this treatment is scientifically proven for outstanding results and each of the modes of energy have a slightly different tissue interaction.
1. High Voltage Pulsatile Currents
This current is used to repair and renew muscle fibres, improving muscle tone and skin elasticity. The clinical efficacy of this technology is known for it’s comfortable delivery of energy which has a stimulatory effect on the nerves of the muscles and promote muscle contraction. This tones and firms muscle laxity whilst regenerating muscle cell function (Alon, 1987).
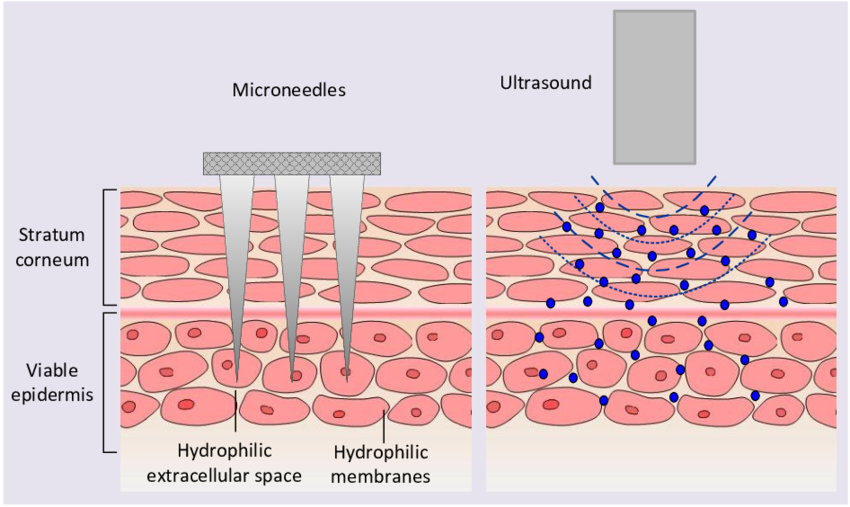
2. Ultrasound
1MHz ultrasound gently heats the tissue in the dermis initiating collagen remodelling and skin tightening. This also allows for movement of molecules between the cells via cavitations or channels and this begins the product delivery. Ultrasound increases the mobility of movement of ingredients through the skin by the vibrational impact sound waves have intercellularly. The energy produced from this vibration generates as heat which has a beneficial relaxation of vasculature stimulating circulation and metabolic processes (Robertson et al., 2006). Phonophoresis or sonophoresis is the method of using ultrasound to create the movement of drugs through the skin to the desired target. Sonophoresis relies on the disturbance of the tissues from the vibrational effects of ultrasound so that molecules can move rapidly between the cells and also into the cells as the cellular membrane becomes disrupted momentarily. Active components are able to be delivered in a very specific way to maximise the impact (Cagnie et al., 2003).
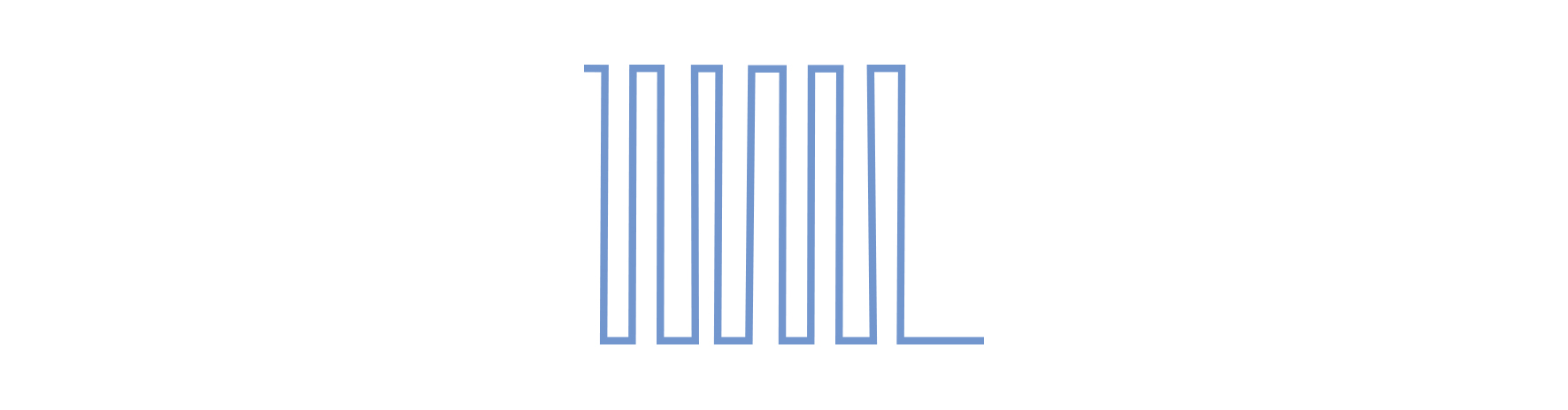
3. Impulsed microcurrent
Microcurrent stimulates muscle contraction and activates cellular ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the “battery” of the cell. Increased ATP production stimulates cellular metabolism which starts to decline with intrinsic and extrinsic ageing factors.
Microcurrent re-educates the muscle fibres and improves blood and lymph flow, restores elasticity, reduces inflammation and erythema, minimises post-surgical recovery time and increases collagen and elastin production (Gerson et al., 2009).
4. Electroporation
The combination of phonophoresis, electroporation and iontophoresis current is the innovative method of increasing the delivery of active nutrients into the skin at depths never reached before. Electroporation “creates new aqueous pathways” through the lipid bi-layer barrier of cells (Weaver & Chizmadzhev, 2018). This temporary interruption of the cell membrane allows active molecules to enter the cytoplasm where they exert potent positive effects. This is the ultimate in transcellular delivery!
5. Iontophoresis (galvanic current)
Iontophoresis is used to “drive” active water soluble particles through the skin without trauma. The penetration is via sweat glands and hair follicles (Robertson et al., 2006). This is specifically important for the delivery of antioxidants and cell renewing peptides into the areas where they are needed most. Particularly beneficial for transcutaneous delivery to treat pigmentary disorders, sun damage and hydration issues.